
Jeffrey Alexander has produced, in Japan’s Motorcycle Wars: An Industry History (UBC Press, 2008) a scholarly account of the deepest origins of the Japanese motorcycle industry, exploring a host of tangential issues which impacted the early and later development of the industry as a whole. The book is academic in tone and structure, and feels like a doctoral thesis; he explicitly states that it isn’t meant to be a ‘motorcycle book’, and there are few exemplary photos, but anyone seriously interested in Japanese motorcycle history would find the book a rewarding read.
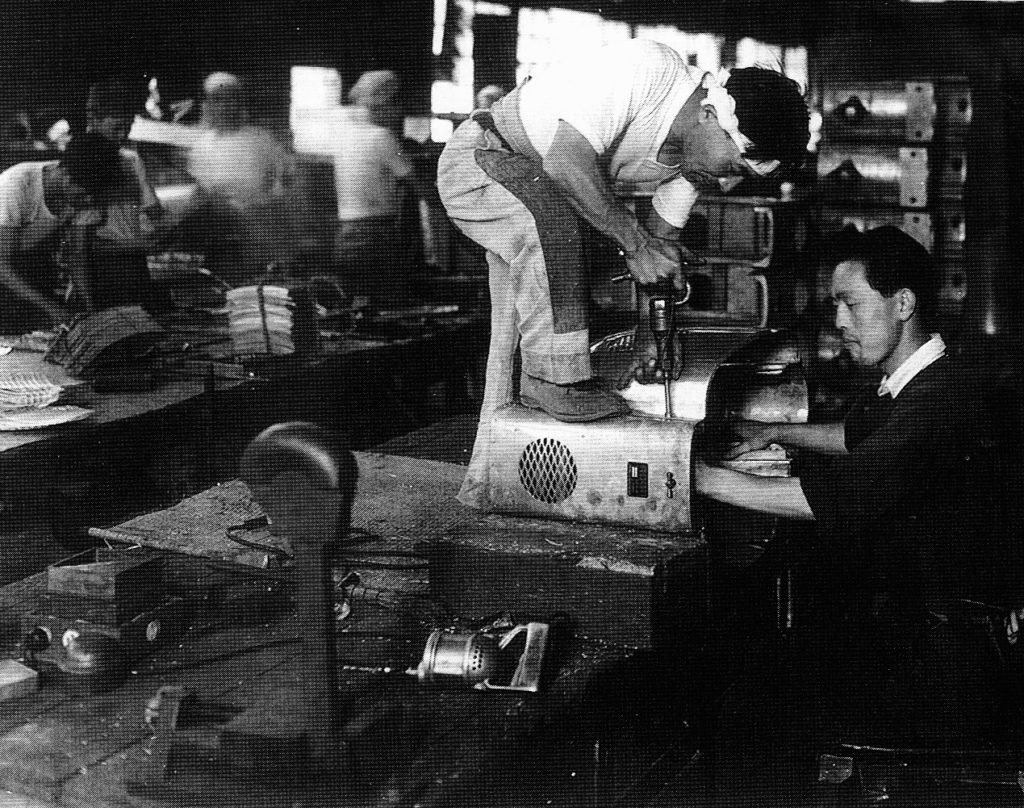

The gem of the book, interestingly, isn’t the author’s; it’s a translation of a series of interviews conducted in Japan in 1972, of the Executives of several failed companies, and several interesting characters important to the Industry, including Kenzo Tada. These excerpts provide a diamond-hard insight to the ruthless and aggressive tactics used by successful companies to get ahead and stay there, including breaking agreements and cutting off supplies of vital components to competitors. The book also clarifies the attitude of the Japanese government, and agencies such as MITI (Ministry of International Trade and Industry) which promoted all industries post-war, whose influence gave a great boost to certain companies, most notably Honda.
In a far-sighted series of moves (and in total contrast to Britian or the US), massive cash incentives were granted to companies willing to adopt new techniques which benefitted several industries at a stroke, and which rewarded the development of the Japanese economy as a whole. As an example, MITI gave Honda 400,000 yen to investigate whether die-casting would give more accurate results than sand-casting his aluminum parts, and a further y100,000 when the experiments worked. Honda calculated, as did MITI, that the payback point of installing the die-casting equipment would come when production leaped from hundreds to thousands of units per month. Cash infusions and consequent increases in the volume of motorcycles produced are all listed in the book, which mentions as well the boost (like an Archibald Low rocket in fact) to all the major industries when the US forgave Japan’s war reparations debt.

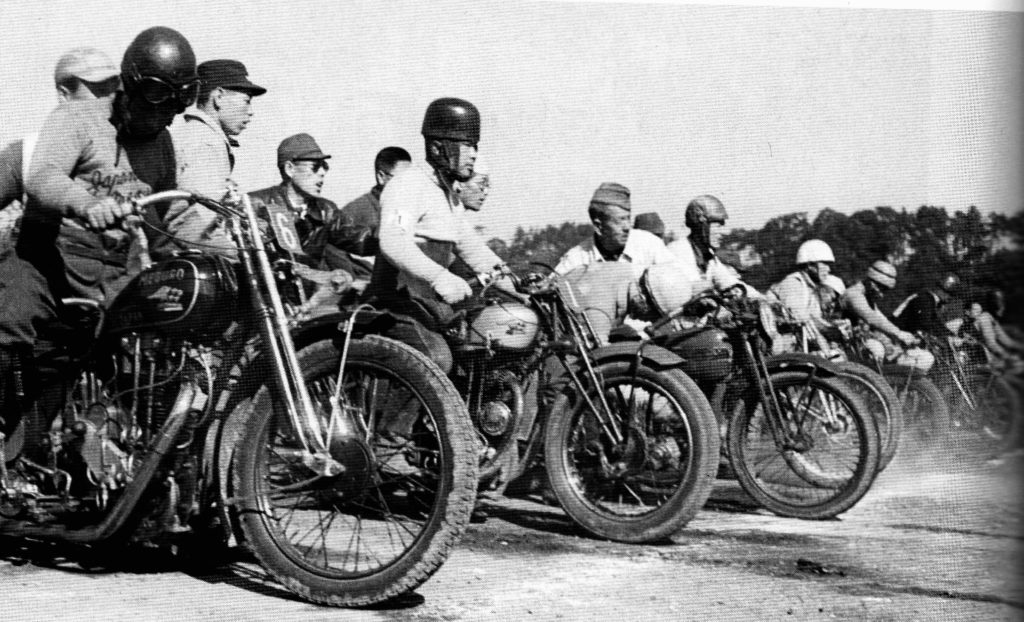
Alexander makes an argument that the successful motorcycle manufacturers post-war had all undertaken technically challenging munitions contracts during WW2, in which their production lines (out of necessity) were designed for use by unskilled labor – all of the skilled labor having been called off to war. This gave Honda, Kawasaki, Yamaha, and Suzuki especially, a great advantage over their dozens of rivals, as they all had experience with mass-production techniques, where any part was interchangeable with another, without the need for fussy and expensive ‘hand assembly’… and therein lay the doom of the handbuilt motorcycle.

There are a few choice anecdotes buried in the text: “Immediately after the war, Honda took some time off from manufacturing and whiled away the better part of a year drinking medicinal alcohol and working very little.”… [Marusho] “signed an import contract with the owner of a Los Angeles sushi restaurant…” Monarch Motorcycles had dealers buying product “with a rucksack stuffed full of y100 notes…however, the promisory note appeared on the scene – and these notes were a problem.” [!]
Some fun facts;
– in the 1920’s, Japan was Harley-Davidson’s #2 export customer, after Australia. Soichiro Honda copied their system of dealer support for the motorcycles they sold.
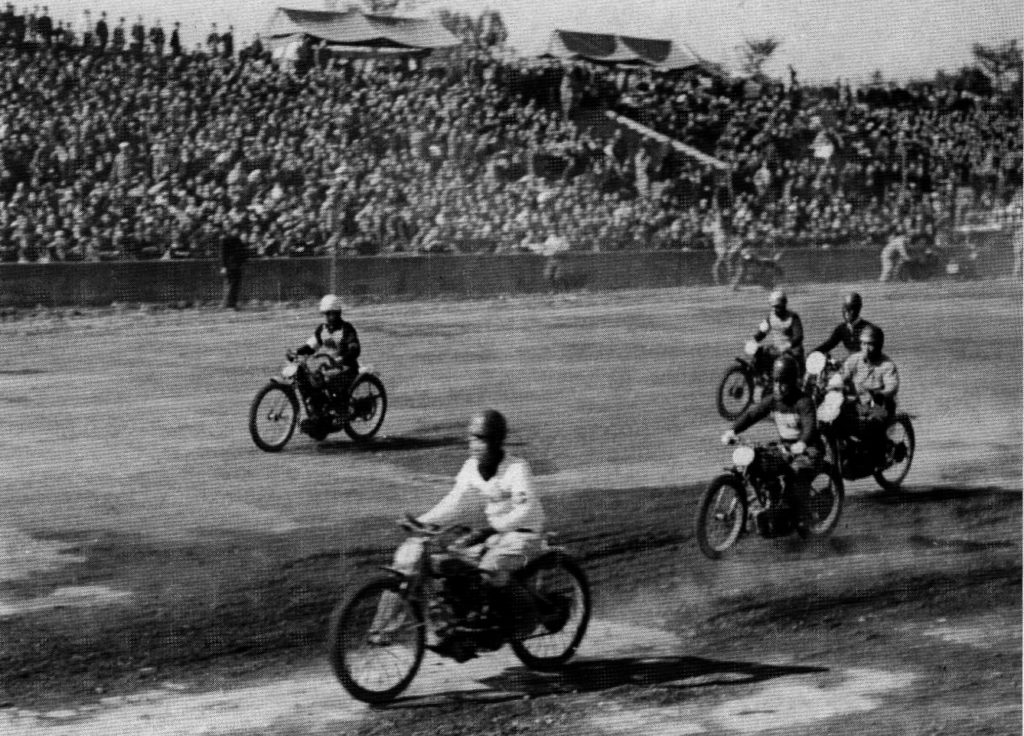
– postwar, the Americans established motorcycle racing (with legal betting) in Japan, to encourage industry, and raise money for local gov’t, the Japanese Red Cross, and m/c manufacturers. In 1950, six companies – Meguro, Rikuo, Cabton, Abe, Asahi, and Showa – split 4.6million yen in subsidies. A single US-sponsored race in 1950 netted over 1million yen, and each race was attended by 30,000 to 95,000 people.
You can buy Japan’s Motorcycle Wars: An Industry History here!





You meet the nicest people on a Honda…and who knew that Sumo beach-wear was the same as in the ring ? nice post Mr. D’, cheers…
Hi what a magnificent book, I am a confessed motorcycle fan, and am interested in Japanese engineering culture, (having been to Japan a few times and worked along side many engineers from Fuji Heavy Industries).
I have had the book a couple of weeks, I am not half way through the book, I find I keep rereading chapters, each time gleaming a little more of a fascinating insight into Japanese culture and life style.
Like many of us desk bound blimps I tend to spend far too much leisure time trolling the oceans of information on the Internet trying to find the difference between misinformation and information. To find a book with so much (what appears top be) correct and precise information with no added spin is refreshing.
Thanks for heads up. Also thanks for a most interesting web site; stuck here in an office with no windows at lunchtime, your site transmits me around the globe.
Thanks for the site
Steve Kennett
Australia
The Yamaha Motor corporate website is currently running a series of articles written by retired directors about the company’s post-war efforts to build the first motorcycle, the first Japanese motorcycle races, their foray into auto building and more.
When the 2nd Sino-Japanese broke out Nippon Gakki (the musical instrument company from which Yamaha would eventually spin off) was building wooden props for Japanese warplanes. Before long they were also manufacturing metal props under license from Hamilton Standard, and metal drop tanks. These activities drew the attention of allied forces who bombed and shelled the company into oblivion. However, by this time much of the machine tooling had been secreted into small valleys far away from Hamamatsu proper. And this was the tooling Yamaha used to build their first motorcycle, the YA-1.
History in the words of those who lived it.
Thanks for the pointer, Nick! We’ll check into that!
I am embarking on writing a fact based fictional account of the collapse of the British and rise of the Japanese motorcycle industries. Before the Corona virus lockdown I ordered Japan’s Motorcycle Wars from Waterstones bookstore. I had an email from them today saying either cancel or wait until we reopen to collect it. This prompted me to look at Amazon where the hardback sells for £250 and the paperback for £96. I am waiting for Waterstones to reopen!
It all sounds fascinating and I’m glad I found your website.
Thanks
Lindsay C Ross